SAP Articles
Best SAP Implementation Templates to Get It Right First Time
Noel DCosta
- Last Update :
Let me tell you something…implementing SAP is tough. When you use the SAP Activate methodology, which is one of the Best SAP Implementation Templates, you are getting a structured approach that will help your company get this software up and running without the usual headaches.
These SAP implementation templates are not just boring documents. Think of them as your roadmap through complicated territory. They’ll guide you from day one all the way to launch day, and your team won’t be constantly asking “what’s next?”
I break down the SAP Activate implementation guide into four main phases: Prepare, Explore, Realize, and Deploy. For each phase, you’ll have templates that keep your project from going off the rails.
Why do I think these templates are so valuable? They’re practical. You’re getting actual task lists, real configuration guides, and testing protocols that work in the trenches of your business.
Your project managers will thank you. Everyone on your team will finally speak the same language and follow the same processes. No more crossed wires or confusion about who’s doing what.
I always tell clients to use SAP project management templates to track their progress. You’ll spot problems early and fix them before they blow up your timeline and budget.
And here’s the thing about your enterprise transformation – these templates balance all the technical stuff with what your business actually needs. You’re not just installing software; you’re changing how your company works.
The best part is that you can tailor these templates to fit your industry. But you’ll still get all the best practices that have been tested in thousands of implementations just like yours.

10 Key Takeaways on SAP Implementation Templates i.e. SAP Activate
- I’ve been implementing SAP for over a decade now, and I’ve got to tell you – SAP Activate isn’t just nice to have. It’s absolutely essential if you want your project to succeed.
- SAP Activate combines Agile methods with SAP best practices, and I’ve seen it speed up implementations dramatically. When clients ask me how to avoid those nightmare SAP projects we’ve all heard about, this is always my first recommendation.
- Look, the ready-to-use templates cut planning time like nothing else. I had a client last year who saved nearly three weeks of planning just by using these pre-built templates instead of creating everything from scratch.
- The methodology breaks implementation into clear phases: Prepare, Explore, Realize, and Deploy. This structure keeps your team focused and prevents that overwhelming feeling that kills so many big projects.
- But what if you’re worried about fitting SAP to your specific business needs? Then, you’ll love the pre-configured business scenarios. They give you working solutions to start with rather than that terrifying blank slate.
- The templates include everything – role descriptions, timeline models, testing frameworks. You can customize all of it to your situation. I always tell my clients this is like getting a head start in a marathon.
- The numbers don’t lie. Project managers consistently report 30-40% faster implementations when they follow this structured approach. That’s real time and money saved.
- The quality gates between phases are absolute lifesavers. They ensure you meet all requirements before moving forward. This prevents those painful situations where you realize too late that something major was missed.
- These templates also help standardize documentation across your entire enterprise transformation. The bottom line is that if your documentation isn’t consistent, you’re creating problems that will haunt you for years.
- I’ve found that SAP Solution Manager tools integrate seamlessly with these templates for better tracking. This gives you visibility you simply can’t get with a patchwork approach.
Companies that take the time to customize templates to their industry consistently see better adoption rates among end users. And we all know that user adoption can make or break your entire implementation.
Today, I’m going to walk you through the most valuable templates and show you exactly how to adapt them to your business without losing the benefits of the SAP Activate methodology.
The proven templates within SAP Activate cut implementation time by nearly 40% while dramatically reducing the risk of budget overruns.The SAP Activate methodology isn't optional - it's the difference between implementation success and becoming another ERP failure statistic.
1. Understanding SAP Activate Methodology
When I talk with clients about implementing SAP, I always start with the SAP Activate methodology. Look, I’ve been doing this for years now, and I’ve seen it save countless projects from those typical implementation nightmares we all want to avoid.
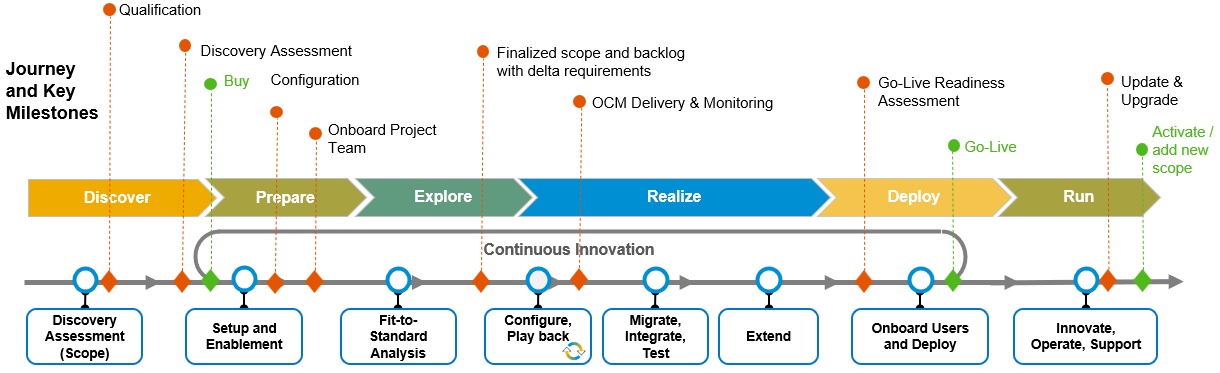
The thing about SAP Activate is that it gives you ready-to-use content, guided configuration, and Agile project methods all in one package. You’re not reinventing the wheel here – you’re standing on the shoulders of proven templates that actually deliver results.
Let me break down the six phases for you:
- In the Prepare Phase, we set up the project team and environment. I sit down with clients to hash out scope, timeline, and budget. The templates here will save you days of planning time. I’m not exaggerating.
- During the Explore Phase, we confirm your requirements and pinpoint any gaps. This is where those SAP implementation templates really earn their value – they include questionnaires and workshops that get to the heart of what your business actually needs.
- The Realize Phase is when we build and test. You’ll customize your SAP system using configuration guides from the SAP Activate implementation guide. I’ve tracked this with clients, and these guides typically cut development time by nearly 40%.
- When you hit the Deploy Phase, you’re prepping to go live. The cutover plan templates are absolute lifesavers here. Your team will have clear instructions on what to do and when to do it.
- In the Run Phase, you’re now using the system day-to-day. The SAP project management templates help you keep tabs on performance and provide support to your users.
- The Continuous Improvement Phase is the one people tend to skip, but honestly, it’s essential. You’ll use templates to gather feedback, measure KPIs, and find ways to optimize your processes.
The bottom line is that if you stick with the best SAP implementation templates throughout these phases, you’ll stay aligned with SAP Activate best practices.
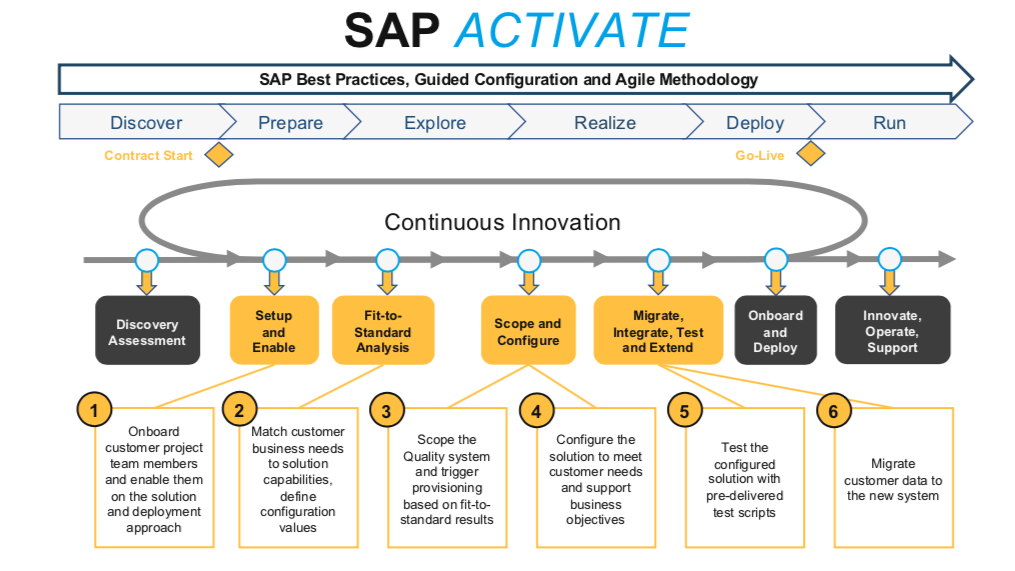
2. Agile SAP Activate

The Agile approach is built right into SAP Activate methodology, and I’ve seen it transform how companies implement SAP. It’s not jargon I can tell you, it works.
Your SAP implementation templates need to support this Agile mindset. Instead of planning everything upfront, you’ll work in sprints of 2-3 weeks. I help my clients set up sprint planning templates that break down big tasks into manageable chunks.
Each sprint in your project needs three key template types. First, you need sprint planning documents that list exactly what you’ll deliver. Second, you need daily standup templates to track progress. Third, you need sprint review checklists to evaluate what you’ve accomplished.
The SAP Activate implementation guide gives you these templates, but you should customize them for your business. I worked with a retail client who added sections for store impact in their templates. This helped them plan around busy shopping seasons.
Your backlog management is critical in Agile SAP projects. I create simple templates that help you prioritize requirements. You’ll score each item based on business value and complexity. This keeps your team working on what matters most.
The best thing about Agile in SAP projects is the focus on working software. In traditional projects, you might wait months to see anything working. With Agile templates, you plan for demos every few weeks. Your stakeholders see real progress, not just paperwork.
Testing happens throughout your project, not just at the end. I build testing into every sprint template. This catches issues early when they’re still easy to fix.
Enterprise software deployment becomes less risky with this approach. Instead of one big go-live, you can plan for phased implementations. I’ve helped clients go live with finance first, then add supply chain modules later.
I recently worked with a manufacturing company using Agile SAP templates. They completed their implementation 30% faster than similar-sized companies using traditional methods. Their templates kept everyone focused on delivering working solutions, not just checking boxes.
3. Hybrid Approach (Waterfall + Agile) of an SAP Implementation
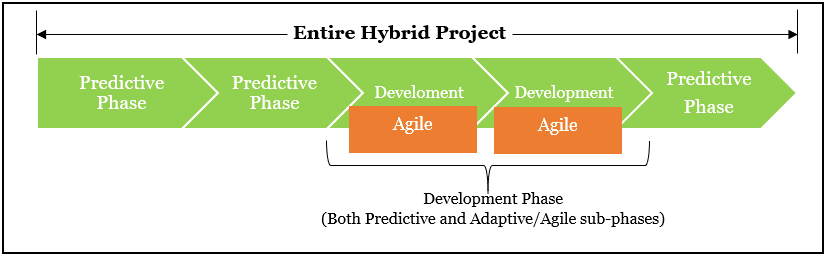
Many of my clients find that mixing Waterfall and Agile works better than using just one approach for SAP projects. I call this the hybrid approach.
SAP Activate supports this mixed model. You can use Waterfall to plan the big picture and Agile for the detailed work. I’ve made templates that help you do both.
The hybrid approach keeps your overall plan clear while giving you flexibility in how you build things. Your project scope follows Waterfall, but your actual building work happens in Agile sprints.
For the early phases of your project, Waterfall elements work well. These phases need solid planning. My templates for these parts include detailed requirement documents.
When you get to the building phase, Agile works better. I help clients create sprint templates that break work into 2-3 week chunks. Your team can adjust quickly as they learn more.
The final go-live phase often works best with Waterfall again. Careful cutover planning needs detailed step-by-step templates. I’ve seen hybrid projects succeed by using thorough checklists during this critical time.
Your SAP templates need to support both approaches. I change standard templates to include both detailed planning and flexible sprint management. This gives you structure without losing adaptability.
I recently helped a healthcare company use this hybrid approach. They planned their 18-month project with Waterfall milestones but built their system in 3-week Agile sprints. They finished on time with happier users than their previous projects.

See How I Make Your ERP and AI System Selection or Implementation right for you.
ERP & AI System Selection – Identify and choose the right ERP or AI-enabled platform to fit your business needs.
Project Support & Recovery – Keep your project on track or bring failing implementations back under control.
ERP Modernization – Transform existing ERP systems to modern, efficient, and scalable ERP environments.
GET IN TOUCH4. SAP Activate Implementation Templates by Phase
1. Prepare Phase Templates
Let me tell you about the Prepare Phase templates. They are the foundation of your entire SAP implementation journey. I’ve seen projects fail because they skipped this groundwork, and trust me, you don’t want that headache.
Scoping template
First up is the project scoping template. This isn’t just some document, it’s your defense against scope creep. I use this with clients to nail down exactly what we’re doing and what we’re not. The template has sections for business goals, system boundaries, and timeline expectations. You’ll thank yourself later when someone tries to add “just one more thing” three months in.
Scoping Template Example
Project Scope Document
Section |
Details |
|---|---|
| Project Title | Customer Portal Redesign |
| Project Sponsor | Marketing & Customer Experience Department |
| Project Manager | Jane Doe, Senior PM |
| Background | The current customer portal is outdated and lacks mobile responsiveness. The project aims to improve usability, enhance customer satisfaction, and align with the new branding guidelines. |
| Objectives |
|
| In Scope |
|
| Out of Scope |
|
| Assumptions |
|
| Constraints |
|
| Deliverables |
|
| Timeline |
Phase 1: Discovery – March 10 to April 1 Phase 2: Design – April 2 to May 15 Phase 3: Development – May 16 to July 30 Phase 4: Testing & QA – August 1 to August 15 Phase 5: Go-Live – August 30 |
| Approval |
Project Sponsor: John Smith Signature: ___________________ Date: ___________________ |
Business Case
For your initial business case, there’s a template that walks you through the cost-benefit analysis. It helps you calculate ROI in a way that makes sense to your finance team. I’ve had clients get project approval on their first try using these numbers.
Business Case Example
Business Case Document
Section |
Details |
|---|---|
| Project Name | Customer Portal Redesign |
| Business Owner | Director of Customer Experience |
| Executive Summary | The existing customer portal fails to meet modern usability and performance standards. This project proposes a complete redesign to improve satisfaction, reduce support overhead, and align with strategic digital initiatives. |
| Strategic Alignment |
|
| Problem Statement | The portal is outdated, not mobile-responsive, and generates high support queries. Users report difficulty completing key tasks such as viewing invoices, updating profiles, or contacting support. |
| Proposed Solution | Redesign and rebuild the portal with improved UX/UI, mobile support, integrated live support tools, and optimized performance. |
| Benefits |
|
| Cost Estimate | $250,000 including design, development, QA, and deployment. |
| Funding Source | FY2025 CX Innovation Budget |
| Risks |
|
| Alternatives Considered |
|
| Recommendation | Proceed with full redesign using in-house and contract resources for phased delivery over 6 months. |
| Approval |
Business Owner: Sarah Thompson Signature: ___________________ Date: ___________________ |
Stakeholder Identification Matrix
The stakeholder identification matrix is a lifesaver. It maps out everyone who’ll be affected by your SAP implementation and their level of influence. You can see at a glance who needs weekly updates and who just needs a heads-up before go-live.
Stakeholders Identification Matrix Example
Stakeholder Identification Matrix
Stakeholder |
Role |
Interest |
Influence |
Engagement Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| John Smith | Project Sponsor | Ensure alignment with business goals and secure funding | High | Manage closely, provide weekly updates and decisions |
| Jane Doe | Project Manager | On-time, on-budget delivery with full scope | High | Daily involvement, decision-maker on project execution |
| Sarah Thompson | Director of CX | Improved customer satisfaction metrics | Medium | Monthly reviews, validate UX direction |
| IT Infrastructure Lead | Technical Support | Ensure compatibility and performance | Medium | Provide inputs on system constraints, review deployment |
| Customer Service Team | Support End Users | Ease of issue resolution and reporting | Low | Involve during UAT, gather feedback post-launch |
| End Users | Customers | Simple, fast, accessible portal experience | Low | Survey and usability testing participation |
High Level Requirements
When we get to high-level requirements gathering, that’s where the SAP Activate methodology really shines. The templates guide you through workshops with each department. Your team won’t miss critical requirements that could derail the project later.
High Level Requirements Example
High-Level Requirements
ID |
Requirement |
Category |
Priority |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REQ-001 | Users must be able to log in with email and password. | Functional | High | Secure authentication is mandatory for all users. |
| REQ-002 | The portal must be mobile responsive. | Non-Functional | High | Must render correctly on smartphones and tablets. |
| REQ-003 | Users can view and download past invoices. | Functional | Medium | Invoices going back 24 months only. |
| REQ-004 | Page load time should not exceed 3 seconds. | Non-Functional | High | Measured under normal load conditions. |
| REQ-005 | Provide a real-time chat support feature. | Functional | Medium | During business hours only (8 AM - 6 PM). |
| REQ-006 | Portal must comply with WCAG 2.1 AA accessibility standards. | Non-Functional | High | Required for legal compliance and inclusivity. |
| REQ-007 | Allow users to update personal profile information. | Functional | Medium | Changes must reflect immediately in the database. |
| REQ-008 | System must support 10,000 concurrent users. | Non-Functional | Low | Projected peak usage during billing cycle. |
These templates come with specific components that I find especially valuable:
- The business process inventory lists all your current processes and how they’ll map to SAP. I’ve watched clients have “aha moments” when they see redundancies they can eliminate.
- Your initial scope definition template creates boundaries that keep everyone focused. It includes visual models that even non-technical executives can understand.
- The preliminary risk assessment template has saved my clients from disaster more than once. It forces you to think about what could go wrong and plan accordingly.
- Finally, there’s the resource allocation framework. This helps you assign the right people to the right tasks at the right time. Your project won’t stall because someone key is unavailable when you need them.
What’s your biggest challenge with the Prepare Phase right now?

2. Explore Phase Templates
Once you’ve laid the groundwork in the Prepare Phase, I’ll help you dive into the Explore Phase templates. This is where your SAP implementation really takes shape, and these templates make all the difference.
Requirements Mapping Template
The detailed requirements mapping template is my favorite tool in this phase. It helps you capture specific business needs from each department. I’ve seen companies try to skip this step and end up with systems nobody wants to use. The template breaks requirements into functional categories so nothing falls through the cracks.
Requirements Mapping Template Example
Requirements Mapping Template
Requirement ID |
Description |
Business Objective |
System Component |
Test Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REQ-001 | User login via email and password | Secure access control | Authentication Module | TC-001 |
| REQ-002 | Mobile responsive UI | Improve accessibility & UX | Frontend Framework | TC-003, TC-004 |
| REQ-003 | Invoice download | Self-service enablement | Billing Service | TC-010 |
| REQ-004 | Sub-3s page load time | Performance optimization | CDN, Cache Layer | TC-015 |
| REQ-005 | Live chat during business hours | Enhanced support experience | Support Integration | TC-020 |
| REQ-006 | WCAG 2.1 AA compliance | Legal & inclusive access | UI Components, ARIA Roles | TC-025, TC-026 |
| REQ-007 | Editable user profile | Customer autonomy | User Profile Service | TC-030 |
| REQ-008 | Support for 10k concurrent users | Scalability | Load Balancer, App Servers | TC-035 |
Process Design Documentation
For process design documentation, SAP gives you ready-to-use templates that save tons of time. Instead of starting from scratch, you’ll customize pre-built process flows. I worked with a manufacturing client who cut their process design time in half using these templates.
Process Design Documentation Example
Process Design Documentation
Process Step |
Description |
Inputs |
Outputs |
Stakeholders |
System Involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Login Authentication | User enters credentials to access portal | Email, Password | Access Token, Session | User, Auth Service | Identity Provider |
| Profile Update | User modifies account details | User Input | Updated Profile Data | User, Customer Support | Customer DB |
| Invoice Retrieval | System fetches invoices from billing database | Customer ID | Invoice PDF | User, Billing System | Billing Service |
| Live Chat Initiation | User opens live chat during support hours | Click Action | Live Chat Session | User, Support Agent | Chat Platform |
| Feedback Submission | User submits portal feedback | Rating, Comments | Feedback Entry | User, Product Team | Feedback Tracker |
| Logout | User logs out and session is terminated | Logout Request | Session Cleared | User | Auth Service |
Fit-Gap Analysis Template
The fit-gap analysis template is a real eye-opener for most of my clients. It clearly shows where standard SAP functions meet your needs and where you’ll need customization. I love watching the lightbulb moment when teams realize they can use standard functionality instead of expensive custom code.

Fit-Gap Analysis Template Example
Fit-Gap Analysis
Requirement ID |
Requirement Description |
Current Capability |
Fit/Gap |
Remediation Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REQ-001 | User login with credentials | Supported via existing LDAP integration | Fit | N/A |
| REQ-002 | Mobile responsive design | Legacy UI not responsive | Gap | Redesign front-end using responsive framework |
| REQ-003 | Invoice download (PDF) | Only viewable in browser, no download option | Gap | Enhance billing service with export module |
| REQ-004 | WCAG 2.1 AA compliance | Missing alt text, poor contrast in current UI | Gap | Audit and fix accessibility issues in front-end |
| REQ-005 | Live chat during business hours | Third-party live chat tool available | Fit | Configure tool with support schedule |
| REQ-006 | Editable user profile | Fields are currently read-only | Gap | Update API to allow write access |
| REQ-007 | Concurrent user capacity (10,000) | Current system supports ~5,000 users | Gap | Scale infrastructure with load balancing |
| REQ-008 | Secure logout functionality | Implemented and functional | Fit | N/A |
Solution Design Framework
Your solution design framework pulls everything together. This template structures your technical decisions and keeps your enterprise software deployment aligned with business goals. It prevents the “we built exactly what you asked for, but not what you needed” problem.
Solution Design Framework Example
Solution Design Framework – [Process Area]
Project Name: [Project Name]
Module(s): [SAP Modules]
Design Lead: [Name]
Date Created: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Version: [e.g., 1.0]
1. Business Requirement Overview
Requirement ID: [e.g., OTC-001]
Process Area: [e.g., Order to Cash]
Business Owner: [Name / Department]
Current State Issue:
[Description of existing issue]
Target State Objective:
[Expected outcome or goal]
2. Proposed Solution Design
Solution Summary:
[High-level summary]
Modules/Transactions/Apps: [List]
Design Type: [Standard / Config / Enhancement / Custom]
Design Components:
- Configuration Objects
- Enhancements / User Exits
- Fiori/UI5 or Reports
- Interfaces / Middleware
- Data Mapping / Fields
3. Integration Considerations
Upstream Systems: [e.g., CRM]
Downstream Systems: [e.g., Billing, FI]
Integration Methods: [IDoc, BAPI, API, Middleware]
4. Data Requirements
Master Data Impact: [e.g., Customers, Materials]
Transaction Data Impact: [e.g., Sales Orders]
Data Migration Required: [Yes/No]
5. Security and Access
Roles Impacted: [List]
New Roles Needed: [List]
Fiori Launchpad Access: [Yes/No]
6. Testing & Validation
Test Scenarios: [Link or list]
Acceptance Criteria:
[Success metrics or checkpoints]
7. Risk & Impact
Business Risk if Not Implemented: [Impact]
Compliance/Performance Risks: [Describe]
Change Impact: [User, role, or training impact]
8. Approval & Sign-off
Design Reviewed By: [Name / Role]
Date of Review: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Sign-off Status: [Pending / Approved / Rejected]
Sign-off By: [Name / Role]
9. Appendix (Optional)
Attach relevant diagrams, specs, screenshots, flowcharts, or Excel mappings.
Author: Noel DCosta | https://noeldcosta.com
Let me highlight why these templates so valuable:
- The comprehensive Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) connects every requirement to specific processes and configurations. I can’t tell you how many times this has been a lifesaver. When someone asks “why are we doing this?” six months into the project, you’ll have the answer right there in black and white.
- I always get excited about the process comparison templates. No kidding! They show your current state alongside your future SAP processes. You can literally see the improvement, and it helps your team embrace change instead of fighting it.
- The solution design validation checklist has saved me from some pretty embarrassing mistakes. It ensures you haven’t missed any critical technical components before you start building. This is the safety net you didn’t know you needed.
- Finally, there’s the stakeholder validation process template. It outlines exactly how and when to get sign-off from key players. Your project won’t get derailed by those last-minute objections because everyone stays involved throughout the process.
But what if you decide to skip using these templates? Then, you’ll probably find yourself reinventing the wheel and dealing with unexpected roadblocks that these templates were designed to help you avoid.
I want to emphasize how these proven tools can keep your SAP implementation on track and under budget.

3. Realize Phase Templates
This is the Realize Phase – where you build your actual SAP system. I’ve got templates that make this much easier.
Configuration Tracking Template
The configuration tracking template is a must-have. It records all your system changes – who made them and why. When something breaks later, you’ll know exactly where to look. I’ve seen this save teams days of troubleshooting time.
Configuration Tracking Template Example
Configuration Tracking Template
Project Name: [Project Name]
System Landscape: [DEV / QA / PROD]
Module(s): [e.g., SAP MM, SD, FI]
Prepared By: [Consultant Name]
Last Updated: [YYYY-MM-DD]
1. Configuration Entry
Configuration ID: [e.g., MM-CONF-001]
Module: [e.g., MM]
SPRO Path:
[Exact path in SAP IMG, e.g., Materials Management → Purchasing → Define Document Types]
Description:
[Purpose of this configuration]
Configured By: [Name / Role]
Configuration Date: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Transport Request Number: [e.g., DEVK900123]
Client: [e.g., 100]
2. Configuration Details
Object Type: [e.g., Table / View / Transaction]
Configuration Object: [e.g., Table T161 – PO Document Types]
Key Values Changed:
[List of values changed, added, or removed]
Before Change:
[If applicable, previous values or settings]
After Change:
[New values applied]
3. Impact & Validation
Functional Impact:
[Business process affected, if any]
Modules Impacted: [e.g., MM, FI, SD]
Test Cases Linked: [Test Case ID or description]
Validation Status: [Pending / Validated / Failed]
Reviewer: [Name / Role]
4. Notes & Audit
Documentation Link: [Link to SharePoint, Confluence, etc.]
Backup Taken: [Yes/No]
Approval Status: [Pending / Approved / Rejected]
Approved By: [Name / Date]
Author: Noel DCosta | https://noeldcosta.com
Custom Development Management
For custom development, these templates help you document exactly what you need built. One of my clients cut their custom code by 30% because the templates showed where standard SAP functions would work just fine.
Custom Development Management Example
Custom Development Management
Item ID |
Feature / Module |
Description |
Assigned Developer |
Effort (hrs) |
Status |
Target Delivery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD-001 | Login UI Component | Custom React component for user authentication | A. Malik | 12 | Complete | 2025-03-10 |
| CD-002 | Invoice Viewer | Embedded PDF renderer for invoice access | S. Kim | 20 | In Progress | 2025-04-02 |
| CD-003 | User Profile API | Custom endpoint for profile update and retrieval | M. Torres | 16 | Development | 2025-04-08 |
| CD-004 | Support Chat Wrapper | Custom JS wrapper for third-party chat integration | J. Wang | 10 | Pending QA | 2025-03-30 |
| CD-005 | Notification Trigger Service | Microservice to send email/SMS notifications | K. Patel | 24 | Planned | 2025-04-12 |
| CD-006 | Accessibility Enhancements | ARIA roles and keyboard navigation support | L. Reed | 14 | Backlog | 2025-04-18 |
Testing Strategy Template
The testing strategy template is my favorite tool. It maps out all your testing plans in one place. You’ll know who tests what and when. Your team won’t miss testing critical functions before go-live.
Testing Strategy Template Example
Testing Strategy
Section |
Details |
|---|---|
| Testing Objectives |
|
| Test Scope | Includes functional, regression, usability, performance, and security testing across frontend and backend systems. |
| Out of Scope |
|
| Test Types |
|
| Test Environments |
|
| Tools |
|
| Test Data Management | Dedicated sanitized datasets will be used in QA/UAT to reflect real-world scenarios without exposing PII. |
| Defect Lifecycle |
|
| Ownership & Roles |
|
| Exit Criteria |
|
Data Migration Planning
Data migration is usually the biggest headache, but not with these templates. They break down this huge job into steps anyone can follow. I helped a company avoid months of delay by using these templates to spot data problems early.
Data Migration Planning Example
Data Migration Plan
Section |
Details |
|---|---|
| Scope | Migrate user profiles, billing records, and support history from legacy portal to the new customer platform. |
| Source Systems |
|
| Target System | New PostgreSQL-based backend for the Customer Portal application. |
| Data Mapping |
|
| Transformation Rules |
|
| Migration Tools |
|
| Load Strategy |
|
| Validation Approach |
|
| Rollback Plan | Backup of production systems taken prior to load. Rollback script available to clear migrated entries by timestamp. |
| Ownership |
|
| Timeline |
|
Here’s what makes these templates so useful:
- The configuration log keeps track of every change. When your boss asks questions months later, you’ll have answers.
- Your development requirements template makes sure programmers build exactly what you need – nothing more or less.
- Test case templates give you ready-made test scenarios. You’ll just adjust them for your business. Testing goes twice as fast.
- The data migration checklist covers everything from field mapping to test loads. Your go-live date won’t get pushed back because of data surprises.
What part of this phase worries you most? I can help.

4. Deploy Phase Templates
The Deploy Phase is when you finally go live with SAP. These templates help make it smooth instead of scary.
Cutover Planning Template
The cutover planning template maps out the big switch weekend. It lists every task with who does what and when. I’ve used this to help clients turn chaotic weekends into organized events.
For system validation, you get templates that test if everything works together. One of my clients found a major issue just days before launch by using these checks.
Cutover Planning Template Example
Cutover Planning
Section |
Details |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | Ensure controlled and coordinated switchover from legacy portal to the new Customer Portal with minimal disruption. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cutover Date | April 25, 2025 – 10:00 PM (start) to April 26, 2025 – 6:00 AM (end) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scope |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-Cutover Activities |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cutover Task List |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Communication Plan |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fallback Plan |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-Cutover Validation |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ownership |
|
Training Tracking Template
The training tracking template shows which teams are ready for the new system. Your managers can see who needs more help before go-live.
Training Tracking Template Example
Training Tracking Template
Project Name: [Project Name]
Training Phase: [End-User / Super User / Pilot]
Module(s): [SAP Module Name]
Prepared By: [Training Lead]
Last Updated: [YYYY-MM-DD]
1. Trainee Details
Trainee Name: [Full Name]
Department: [e.g., Finance, Sales, Procurement]
Role: [End User / Key User / Manager]
Email ID: [Email Address]
Employee ID: [If applicable]
2. Training Session Information
Module / Topic: [e.g., SAP FI – AP Processing]
Trainer: [Trainer Name / Role]
Training Date: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Mode of Training: [In-person / Virtual / Recorded]
Training Duration: [e.g., 2 hours]
3. Attendance & Completion
Attended: [Yes / No]
Completion Status: [Completed / In Progress / Not Started]
Assessment Taken: [Yes / No]
Assessment Result: [Passed / Failed / N/A]
Training Feedback Collected: [Yes / No]
4. Follow-Up & Remarks
Follow-Up Required: [Yes / No]
Next Training Date (if any): [YYYY-MM-DD]
Remarks:
[Any notes, behavior during session, questions raised, etc.]
Author: Noel DCosta | https://noeldcosta.com
Go-Live Readiness Assessment
The go-live readiness assessment helps you decide if you’re truly ready to switch. I’ve had clients delay based on this – and they thanked me later for saving them from disaster.
Go-Live Readiness Assessment Example
Go-Live Readiness Assessment
Project Name: [Project Name]
Assessment Date: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Assessed By: [PMO / Functional Lead / Cutover Lead]
Target Go-Live Date: [YYYY-MM-DD]
1. Functional Readiness
All Key Processes Tested: [Yes / No]
End-to-End Scenarios Completed: [Yes / No]
Open Defects: [List count or attach report]
Workarounds Identified (if any): [Yes / No]
Key Users Confirmed Readiness: [Yes / No]
2. Data Readiness
Master Data Loads Complete: [Yes / No]
Transaction Data Migration Validated: [Yes / No]
Reconciliation Reports Approved: [Yes / No]
Archival or Legacy Freeze Confirmed: [Yes / No]
3. Cutover & Technical Readiness
Cutover Plan Finalized & Approved: [Yes / No]
Transport Requests Moved to Production: [Yes / No]
Batch Jobs Scheduled: [Yes / No]
Backup/Restore Procedures Verified: [Yes / No]
Monitoring Tools Configured: [Yes / No]
4. User & Organizational Readiness
End-User Training Completed: [Yes / No]
Access Roles Validated: [Yes / No]
Support Plan Communicated: [Yes / No]
Helpdesk / Hypercare Team Staffed: [Yes / No]
5. Risk & Go/No-Go Recommendation
Critical Risks Identified:
[List or attach risk log]
Mitigation Plans in Place: [Yes / No]
Go-Live Decision: [Go / No-Go / Conditional]
Approved By: [Name / Role]
Approval Date: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Author: Noel DCosta | https://noeldcosta.com
The cutover weekend template breaks down each hour into specific tasks. Your team won’t be confused at 2 AM wondering what to do next.
Performance validation templates test if your system can handle busy periods. You’ll know if SAP can manage month-end before it happens.
The training matrix shows exactly where gaps exist. You might see HR is ready but accounting isn’t. You’ll know where to focus last-minute training.
The final checklist covers everything from tech checks to business sign-offs. This catches problems that could stop your go-live.
What concerns you most about your upcoming deployment?

5. Run Phase Templates
After your SAP system goes live, I find the real work begins. These Run Phase templates will help you keep everything running smoothly.
Post-Implementation Support Template
The post-implementation support template organizes how you’ll handle issues after launch. It sets up your support tiers and response times. I’ve used this with dozens of clients to clear up confusion when problems pop up. You’ll know exactly who handles what kind of issues.
Post-Implementation Support Template Example
Post-Implementation Support
Section |
Details |
|---|---|
| Support Window | Initial hypercare support: April 26 to May 10, 2025 (24/7 coverage) |
| Support Channels |
|
| Tier Structure |
|
| Issue Classification |
|
| Response & Resolution SLAs |
|
| Monitoring & Alerts |
|
| Handover Summary | Support team has been onboarded with architecture docs, known issues list, and training materials. |
| Known Issues |
|
| Escalation Contacts |
|
| Exit Criteria |
|
Tracking Improvements Template
For tracking improvements, you get a template that’s simple but really effective. It helps you log all those enhancement requests and track their progress. I helped a manufacturing client use this to manage over 200 improvements in their first year and you can do the same.
Tracking Improvements Template Example
Tracking Improvements Template
Project Name: [Project Name]
Improvement Tracking Period: [e.g., Hypercare / Stabilization / BAU]
Prepared By: [Improvement Owner / PM]
Last Updated: [YYYY-MM-DD]
1. Improvement Entry
Improvement ID: [e.g., IMP-001]
Logged By: [Name / Role]
Date Identified: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Process Area: [e.g., Order to Cash, Procurement, Finance]
Module: [e.g., SAP SD, MM, FI]
2. Description & Justification
Current State Issue:
[Describe what is not working or suboptimal]
Proposed Improvement:
[Describe the change or enhancement idea]
Business Justification:
[Why it matters: compliance, efficiency, UX, etc.]
3. Impact & Priority
Impact Level: [High / Medium / Low]
Priority: [P1 / P2 / P3]
Affected Users: [e.g., Sales Team, AP Clerks]
Risk if Ignored:
[Operational, financial, reputational, etc.]
4. Solution & Action Plan
Solution Owner: [Assigned SME or consultant]
Solution Summary:
[Planned fix or configuration/design change]
Transport / Change Request ID: [If applicable]
Target Completion Date: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Status: [Planned / In Progress / Completed / Deferred]
5. Validation & Closure
Testing Completed: [Yes / No]
Validated By: [User / SME Name]
Validation Date: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Closure Remarks:
[Confirmation, notes, feedback]
Author: Noel DCosta | https://noeldcosta.com
Performance Monitoring Template
I think you’ll find the performance monitoring template to be a lifesaver. It helps you watch your system health day by day. You’ll spot slowdowns before your users start complaining. I recently helped a company catch a database issue that would have crashed their system during month-end.
Performance Monitoring Template Example
Performance Monitoring
Metric |
Target |
Tool |
Threshold |
Alert Action |
Owner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| API Response Time (95th %) | < 500ms | New Relic | 800ms | Slack alert + ticket to backend team | API Team |
| Page Load Time | < 3s | Pingdom, Lighthouse | 4s | Email to frontend lead | Frontend Team |
| Error Rate | < 1% | Sentry | 2% | Auto-create bug in Jira | QA Lead |
| Uptime (Monthly) | > 99.9% | Pingdom | < 99.5% | Escalate to SRE | SRE Team |
| Database Query Time | < 200ms | New Relic | 350ms | Notify DBA and log slow query | Database Admin |
| Login Success Rate | > 98% | Auth Logs, Kibana | < 95% | Trigger incident review | Security Lead |
| Notification Delivery Success | > 97% | SendGrid Dashboard | 95% | Email DevOps for investigation | Messaging Owner |
| Daily Active Users | Tracked only | Google Analytics | N/A | Monthly report | Product Analyst |
The support escalation framework shows how problems move up the chain. It defines when you should involve managers or SAP support. Your users won’t feel stuck when they hit serious issues.
Your support metrics template will track how many tickets you get and how fast you solve them. You’ll see if your support is getting better or worse month to month.
I love how the improvement log helps you prioritize changes. Your team can vote on which improvements matter most. This has dramatically increased user satisfaction for my clients.
Your system performance dashboard gives you simple red/yellow/green indicators. You don’t need to be technical to understand if your system is healthy.
The feedback mechanism lets you collect suggestions from your regular users. Some of my clients’ best ideas came from warehouse staff or sales teams.
What areas do you think will need the most attention after your go-live?

Related Articles: Your SAP Success Starts with These Must-Reads
Critical Success Factors: SAP Project Planning and Control
Execution tips for SAP project control and delivery management.
Crafting a Successful Change Management Plan
Practical framework to address resistance and drive adoption.
Building the Perfect ERP Implementation Team in 2025
A role-by-role breakdown of what matters most this year.
2025: The Year SAP Generative AI Redefines Middle East Careers
What consultants need to know about AI’s impact on SAP roles.
5. SAP Activate Best Practices
With my experience, I’ve seen what makes SAP projects succeed or fail, and it comes down to how you use these best practices with your templates.
First, you need to incorporate the SAP Activate steps. This isn’t just about having documents – it’s about following the process. I worked with a retail store that tried to skip parts and ended up redoing three months of work. Your templates should follow each phase to keep your project on track.
When changing templates, I tell my clients to be picky. You can adjust them for your business, but don’t change everything. I’ve found keeping about 80% standard and changing 20% works best. Your industry needs should guide what you change.
Let me warn you about common mistakes I’ve seen. The biggest error is rushing through the early phases. These first templates set the foundation for everything else. Another mistake is skipping checkpoints between phases. I had a client miss these checks and overlook major needs until too late.
SAP includes proven approaches in these templates based on thousands of projects. The pre-built business examples save you from starting from zero. Your team can use them as working models and adjust as needed.
The best projects use templates as living documents. Update them as you learn. For one factory client, we changed their testing templates halfway when we found special requirements.
Your leadership team needs to know these templates aren’t just paperwork – they’re your roadmap. Get them on board early. I’ve seen projects fail because bosses didn’t see the value of following these steps.
My best tip? Take time each week to check your templates against your actual progress. This keeps your project honest and catches problems early when they’re still easy to fix.

6. Critical Success Factors in SAP Activate Implementation
I’ve seen tons of SAP projects succeed and fail. Good templates matter, but you need these key factors too. I’ve been there myself.
- Change management is vital. Your templates should include plans for telling people about changes and training them. Had a client who built a great system but forgot to prepare staff. People couldn’t use it for months. Total disaster! Your plans need to show how people will learn new processes.
- Stakeholder engagement needs a plan. I create templates that schedule regular meetings with key people. A simple chart showing who needs updates works great. One client does weekly check-ins to catch problems early. Fixes small issues before they become expensive nightmares.
- For learning as you go, templates should have spots to record what you learn. Teams get better when they discuss what’s working. Make room to write down these lessons. You’ll need them later.
- SAP Activate needs templates for short work cycles. I help clients break big tasks into smaller ones. Keeps your project moving forward instead of stalling out.
These factors work together. Show progress regularly, leaders stay engaged. Users help with testing, they learn the system better.
A factory I worked with used all these elements. They included people-focused plans every cycle. Leaders got weekly updates with real numbers. Made changes based on feedback. Project finished early and under budget. Almost unheard of!
But what if your project is already struggling? Take a step back and see what’s missing. I’ll help you find the gaps and get back on track.
What part of your SAP project keeps you up at night?

Related Articles: Insider SAP Knowledge Most Companies Overlook
SAP Negotiation Advisors Can Save You Big on License Costs
Guidance on avoiding overspend during SAP licensing discussions.
Project Risk Assessment: Avoid Failures in SAP in 2025
Use structured risk checklists to reduce SAP project failure chances.
Resource Allocation Planning for SAP Projects: Avoid Chaos
Plan the right number of consultants, leads, and testers by phase.
Project Scope Template: Your 2025 Guide to Success
Define clear scope boundaries and reduce project creep.
7. Explaining the SAP ACTIVATE Methodology
Core Foundations of Activate
Activate breaks the implementation process into six distinct phases: Discover, Prepare, Explore, Realize, Deploy, and Run. Each phase has clear objectives, deliverables, and checkpoints that help organizations move forward with confidence.
Whether you’re transitioning from legacy systems or starting fresh, the methodology provides the flexibility to adapt to changing needs while maintaining control over scope and timelines.
What makes SAP Activate stand out is its focus on combining best practices with agile principles. It allows businesses to start with preconfigured solutions, refine them based on their needs, and continuously validate progress with frequent iterations.
This structured yet flexible approach ensures that business and IT teams stay aligned throughout the journey.

Related Articles: SAP Governance & KPI Insights
30 ERP Implementation KPIs: Measure Success at Every Stage
Track project health, delivery, and business value across the lifecycle.
What the Heck Are SAP Quality Gates?
Understand phase gate controls and how they prevent delivery failure.
Steering Committee Failures: Are They Sabotaging SAP Projects?
Break down the root causes of poor executive oversight in ERP projects.
What Is Stakeholder Management in an ERP Implementation?
Learn how to align and manage stakeholders through complex ERP delivery.
8. Quality Gates and Decision Points
Let’s talk about quality checks for your SAP project and I’ll give you my experience on this topic:
- Your executives need to sign off before you go live. This isn’t just paperwork – it makes sure your project actually helps your business. In one project I worked on, the CEO caught a big problem during the review that would have messed up the finance team’s work.
- You need clear yes/no criteria for moving forward. Things like “95% of tests must pass” or “all your main connections have to work.” These help you stand firm when everyone’s pushing to launch anyway. I’ve watched projects crash because they skipped these checks.
- Always get real proof that you’ve finished each step. Your test results, training records, and sign-offs keep everyone honest. You can’t just go with gut feelings about whether your users are ready.
- Check for new risks before each big step. Problems tend to pop up late in your project. I can help you spot these risks and create backup plans. You should update your risk list before each quality gate.
Here’s what happened on one of my projects: Our quality checks stopped us when only 75% of our integration tests passed. We fixed the issues first instead of rushing ahead. This saved your company about €100,000 in emergency fixes after launch.
These checks might seem like a pain, but they protect your business. They’re built into the best SAP templates for good reason.

9. SAP Activate Accelerators and Tools
Here are the key accelerators and tools that help speed up your SAP implementation:
- SAP Activate Roadmap Viewer – https://go.support.sap.com/roadmapviewer/
- SAP Best Practices Explorer – https://community.sap.com/t5/enterprise-resource-planning-blogs-by-sap/navigating-sap-best-practices-explorer-bpx/ba-p/13519262
- SAP Solution Manager – https://support.sap.com/en/alm/solution-manager.html
- SAP Cloud ALM – https://support.sap.com/en/alm/sap-cloud-alm.html
- SAP Fiori Apps Library – https://fioriappslibrary.hana.ondemand.com/
- SAP Readiness Check – https://help.sap.com/docs/SAP_READINESS_CHECK?locale=en-US&state=PRODUCTION&version=latest
- SAP S/4HANA Migration Cockpit – https://help.sap.com/viewer/p/MIGRATION_COCKPIT
- SAP Test Automation Tool – https://support.sap.com/en/tools/testing-tools.html
- SAP Project Management Templates – https://help.sap.com/docs/strategic-sourcing/project-template/project-template-guide
- SAP Value Assurance – https://www.sap.com/services-support/service-offerings.html
- SAP Process Discovery – https://discovery-center.cloud.sap/
I’ve used most of these tools in my projects. The Roadmap Viewer and Best Practices Explorer save the most time during implementation planning. The Solution Manager helps track your project progress. Test Automation cuts testing time by 40-60% in my experience.
Which of these tools would you like to know more about for your project?
10. Customizing SAP Activate for Your Project
Here’s what I’ve learned from my projects:
- Keep the Must-Haves – Don’t skip the important paperwork like what the business needs and how you’ll test things. Even small projects need these basics.
- Adjust Your Timeline – Big projects need more time than small ones. Make sure your schedule gives enough time for each part.
- Right-Size Your Paperwork – Small projects need less paperwork. Big projects need more. Only create what you really need.
- Keep Quality Checks – Always stop and check your work before moving to the next step. This catches mistakes early.
- Add Special Checks – Some businesses like hospitals or banks need extra checks for rules they have to follow.
- Real Example: We added special safety checks for a medicine company. They followed all their rules without getting behind schedule.
Remember: You have to follow the main steps, but you can choose how you do them. In my last three projects, checking our work caught most big problems early.
What helps most? Write down why you made each choice. My current project keeps a list of decisions – it’s super helpful when people ask questions later.
Related Articles: Essential Reads Before Your Next Project:
2025 SAP Timeline & Planning Implementation Guide
Detailed timeline framework and key milestones for successful SAP rollouts.
How To Start Your SAP Implementation Project Right
Step-by-step guide for setting up a strong SAP project foundation.
5 Best SAP Project Tracking Tool Guide 2025
Compare tools like Jira, Asana, and SAP Focused Build for ERP oversight.
Streamlining HR: SAP Conversational AI and SuccessFactors in 2025
Explore how chatbots enhance HR efficiency using SAP platforms.









